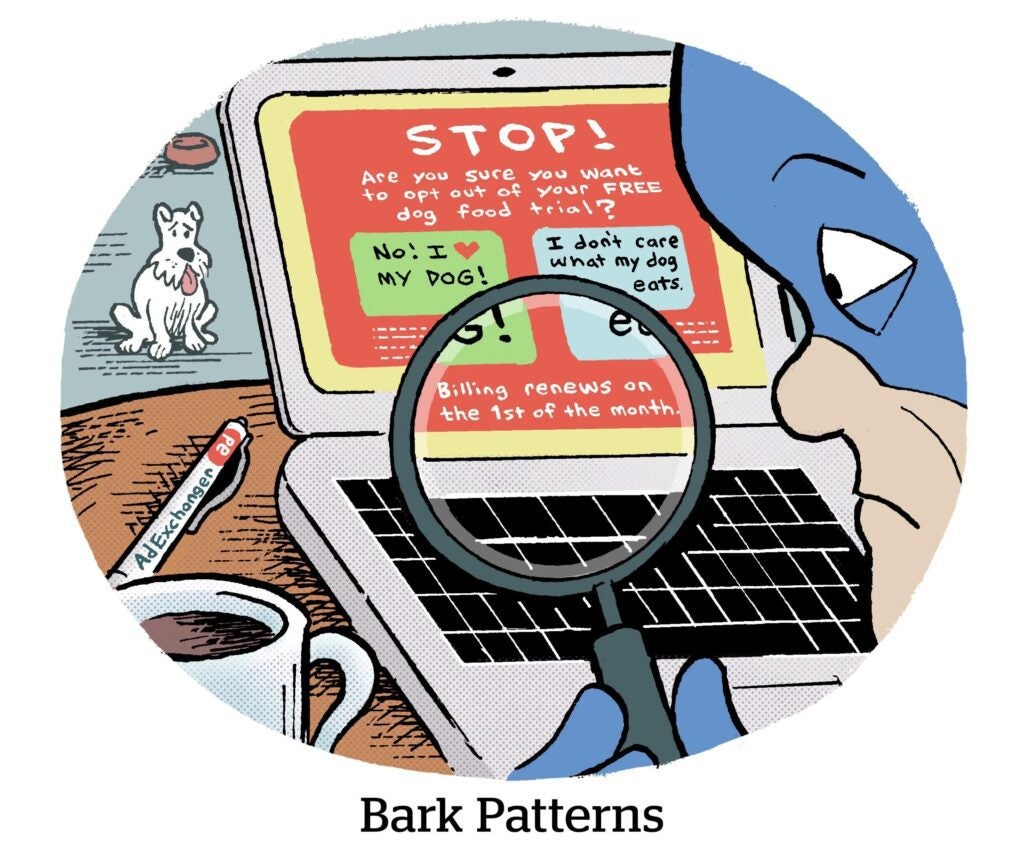
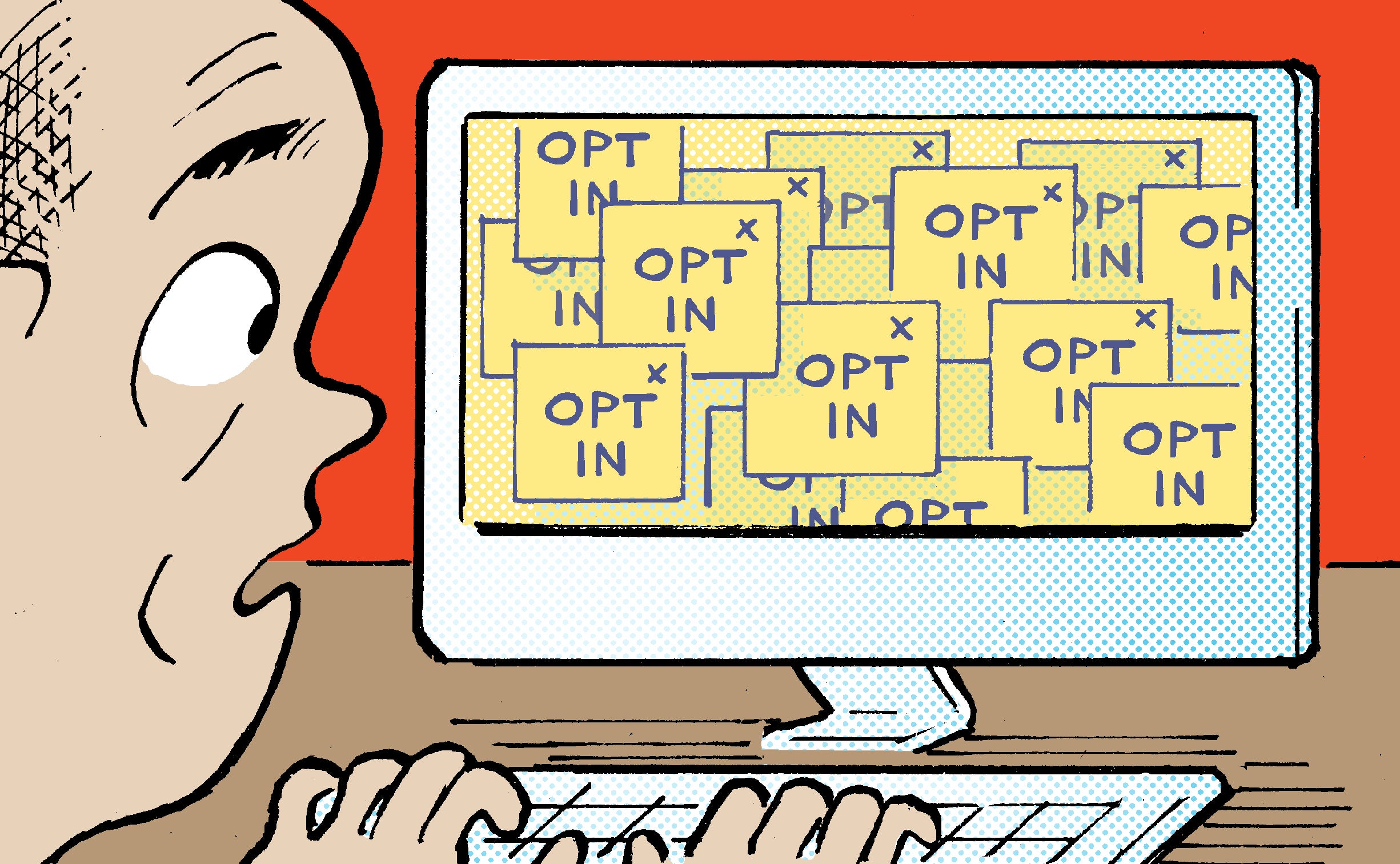
privacy zuckering (noun)
: a dark pattern; the practice of tricking users into disclosing more personal information than they had intended to
Ah, the dubious honor of having an entire dark pattern named after you.
More than five years after GDPR went into effect, regulators in Europe finally exerted enough pressure on Meta that it will soon start asking its users for consent before processing their personal data for targeted advertising purposes.
A win.
Consent is becoming the de rigueur legal basis to process personal data for targeted advertising purposes in Europe, but getting it isn’t so easy. Collecting consent is a far more nuanced process than just getting someone to opt in. It also matters how you ask for it.
Shining a light
To take a step back, dark patterns involve the use of design deception to nudge (or trick) someone into taking an action they otherwise wouldn’t have taken if they fully understood what they were agreeing to.
Dark patterns go far beyond misleading data collection practices to encompass anything from hiding junk fees in a bill to using countdown timers on offers that aren’t actually limited to making it as difficult to cancel a subscription as it would be to solve the Riemann hypothesis. (I assume. I can barely calculate the tip on a restaurant check.)
In June, the Federal Trade Commission (which released a staff report last year about the rise in “sophisticated” dark patterns) filed a lawsuit against Amazon alleging the use of dark patterns to trick consumers into enrolling for Prime.
And later that month, Publishers Clearing House agreed to pay $18.5 million to refund consumers after settling with the FTC over detective sweepstakes practices, including leading people to believe that making a purchase would increase their chances of winning.
Cracking down on dark patterns in all forms is “a huge priority” for federal regulators, said Paavana Kumar, a partner at Davis+Gilbert.
The FTC will have no patience for the use of hidden clauses, vague statements or pre-ticked boxes. Tricking someone into giving their permission isn’t any better than not asking for permission at all.
“No matter whether you’re a marketer, publisher, technology company or retailer,” Kumar said, “if you haven’t been focused on dark patterns to date, now is the time to wake up.”
Because it’s not just the feds that are taking notice.
Numerous state privacy laws, including in Connecticut, Colorado and California (under the CPRA), have prohibitions against the use of dark patterns to obtain consent. As under GDPR in Europe, consent must be unambiguous, informed, specific and freely given.
It’s a “significant trend that state privacy laws are specifically calling out dark patterns as an unlawful data privacy practice,” said Mary Engle, EVP of policy at BBB National Programs.
“As state laws go into effect, I expect we’ll see enforcement actions,” Engle said. “In California, for example, you have to provide symmetry in choice to accept or reject options, [and] I can see that as being low-hanging fruit for enforcement.”
Which is just as true back across the pond.
Dark patterns are on the radar of the Advertising Standards Authority in the UK, the European Data Protection Board and numerous other governmental bodies.
And although GDPR doesn’t explicitly mention “dark patterns,” it also requires that withdrawing consent should be as easy as it was to give it in the first place (which is known as the “mirroring effect”).
This isn’t a radical notion. And neither is respecting a person’s right to understand what the heck they’re agreeing to.
“It comes down to keeping the ordinary consumer in mind when designing your site,” Engle said, “and using simple design and clear, understandable language with the goal of enabling the consumer to easily make choices.”
But make sure to leave any loopholes at the door.
“Remember,” Kumar said, “‘mirror cancellation’ doesn’t mean a 17-step sign-up allows you to offer a 17-step cancellation mechanism!”
Enjoying this newsletter? Got any feedback to share? Bright ideas? (This cat does.) Anyway, let me know what you think. Drop me a line at allison@adexchanger.com.